Issue #525
Use macOS Command Line project
Example Puma
- Create a new macOS project, select Command Line Tool

- Drag
Puma.xcodeprojas a sub project of our test project - Go to our TestPuma target, under
Link Binary with Libraries, select Puma framework
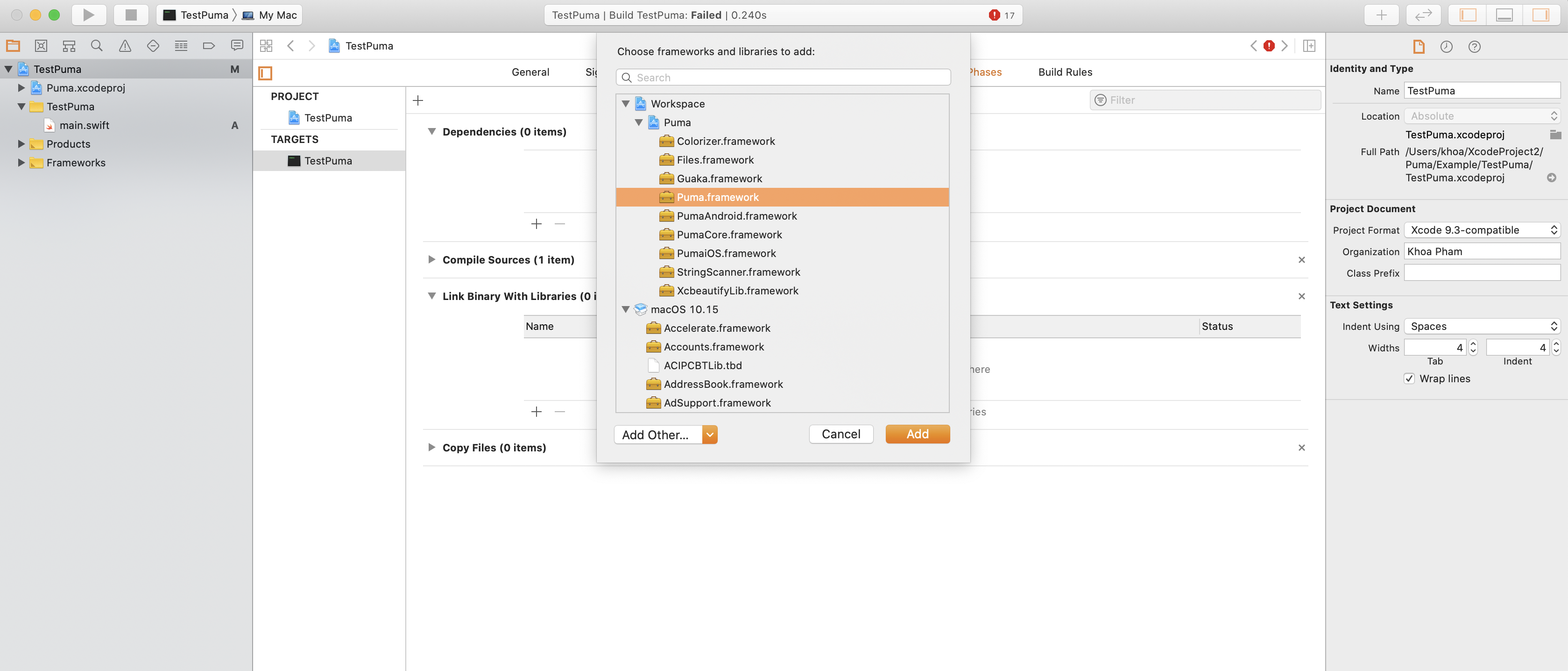
-
Puma has dependencies on PumaCore and PumaiOS, but in Xcode we only need to select Puma framework
-
In code, we need to explicitly import PumaiOS framework if we use any of its classes
import Foundation
import Puma
import PumaiOS
func testDrive() {
run {
SetVersionNumber {
$0.buildNumberForAllTarget("1.1")
}
}
}
- As our Puma.xcodeproj is inside this test project, we can drill down into our Puma.xcodeproj and update the code.
Workspace
Instead of dragging Puma as a subproject of TestPuma, we can use workspace, and link Puma frameworks
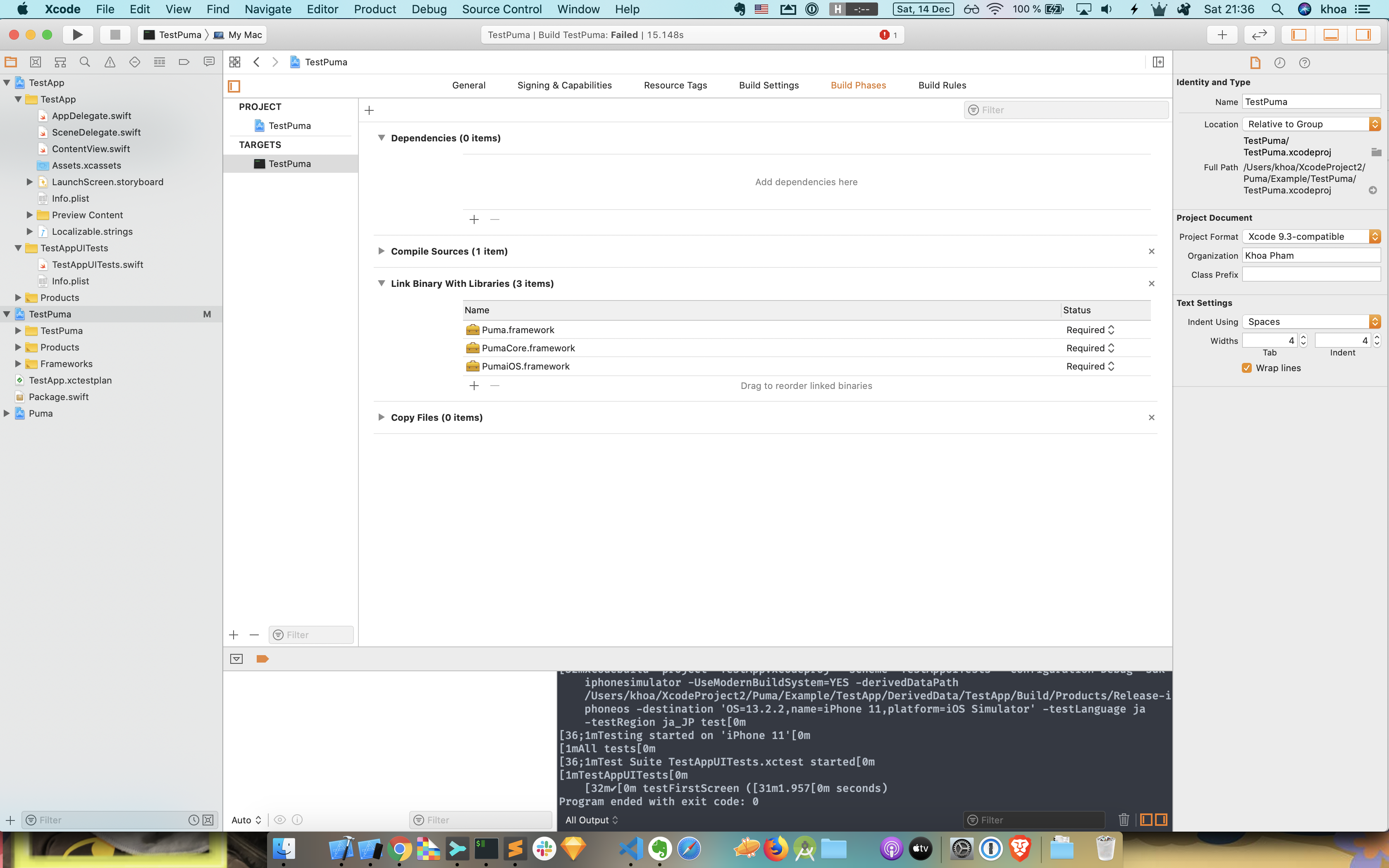
Troubleshooting
Code signing for frameworks
To avoid signing issue, we need to select a Team for all frameworks
not valid for use in process using Library Validation: mapped file has no Team ID and is not a platform binary (signed with custom identity or adhoc?
Library not loaded
Need to set runpath search path, read https://stackoverflow.com/questions/28577692/macos-command-line-tool-with-swift-cocoa-framework-library-not-loaded
Specify LD_RUNPATH_SEARCH_PATHS = @executable_path in Build Settings
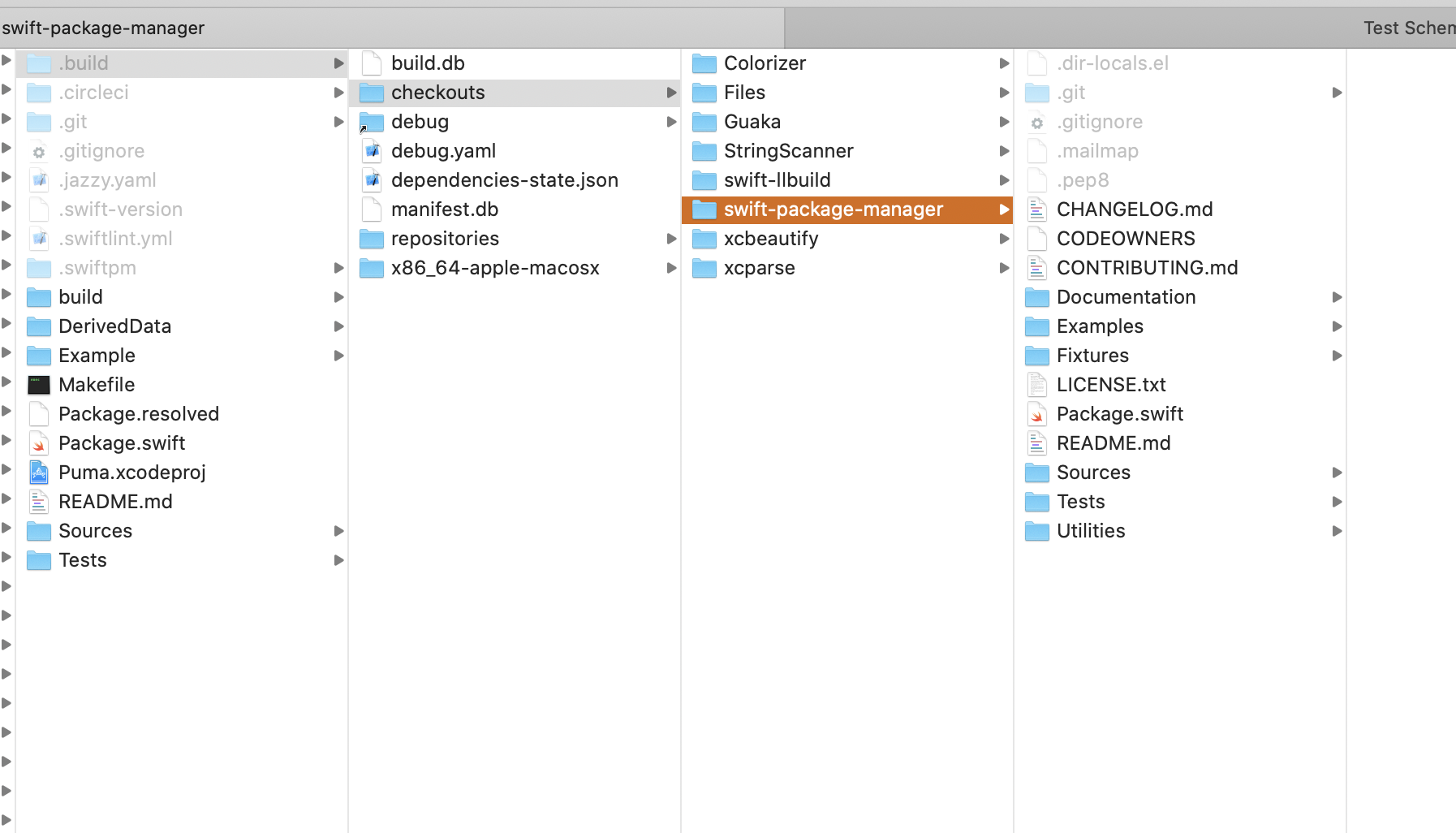
missing required module ‘clibc’
Take a look at Puma -> SPMLibc, there’s header search path
$(SRCROOT)/.build/checkouts/swift-package-manager/Sources/clibc/include
which is at the .build folder inside root
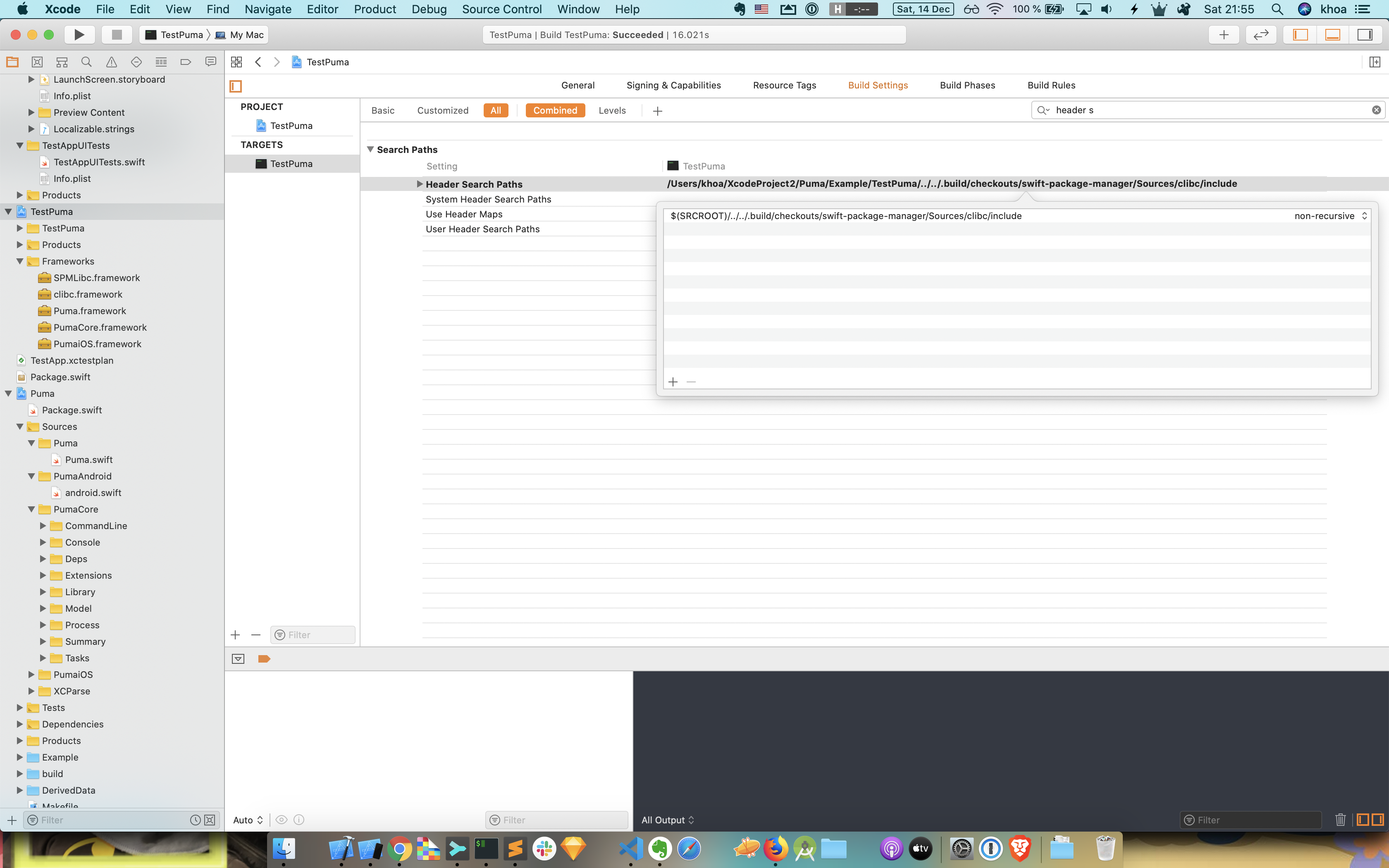
So for our TestPuma target, we need to add this header search path with the correct path
$(SRCROOT)/../../.build/checkouts/swift-package-manager/Sources/clibc/include
Start the conversation